Water quality monitoring is critical for public health, industrial operations, and environmental sustainability. In Sri Lanka, water sampling plays a pivotal role in ensuring clean drinking water, maintaining industrial efficiency, and assessing wastewater treatment systems. By adopting the right techniques and using appropriate water sampling equipment, you can obtain accurate data for effective decision-making.
This blog explores the importance of water sampling, various methods, the correct water sampling procedure for chemical analysis, and best practices for wastewater sampling to maintain accuracy and reliability.
What is Water Sampling?
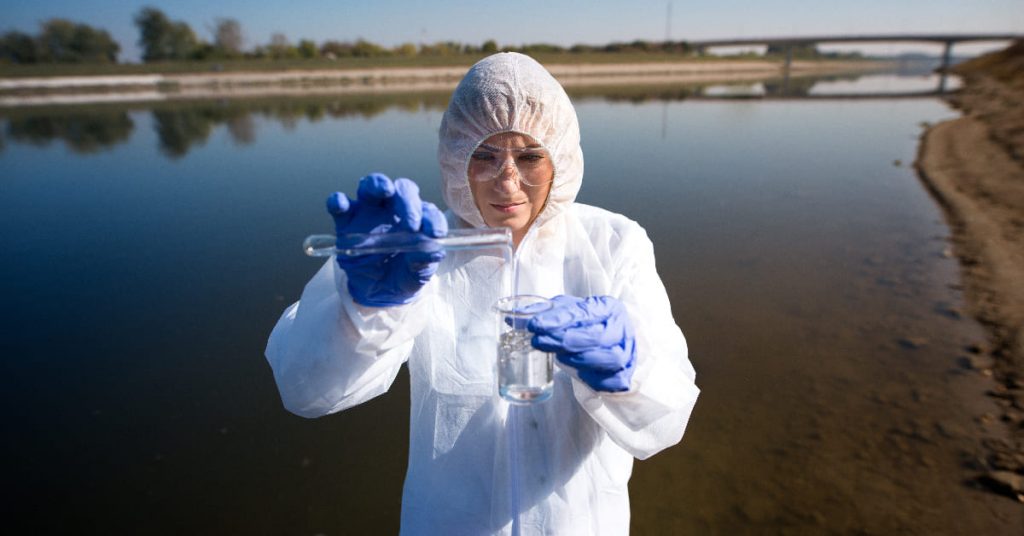
Water sampling is the process of collecting water from a specific source to analyze its quality. It provides essential data about the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water. This information is crucial for assessing pollution levels, determining water safety for human use, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Why is Water Sampling Important in Sri Lanka?
Sri Lanka faces water-related challenges such as contamination from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urbanization. Regular water sampling is essential for:
- Public Health
- Identifying harmful contaminants like bacteria, heavy metals, and nitrates in drinking water supplies.
- Environmental Protection
- Monitoring pollution levels in rivers, lakes, and coastal waters to protect ecosystems.
- Industrial Operations
- Ensuring the quality of process water and wastewater to optimize performance and meet regulatory standards.
- Compliance
- Meeting local and international water quality guidelines to avoid penalties and protect resources.
Types of Water Sampling
Different water sources and objectives require specific sampling methods. The main types of sampling include:
- Grab Sampling
- A single sample is collected at a specific time and location.
- Suitable for small-scale studies or when water quality does not fluctuate significantly.
- Composite Sampling
- Multiple samples are collected at different times and mixed to provide an average representation.
- Commonly used in wastewater sampling for industrial and environmental analysis.
- Integrated Sampling
- Water is collected from various points in a body of water to account for spatial variations.
- Ideal for large lakes, rivers, or reservoirs.
- Continuous Sampling
- Automated water sampling equipment collects samples over time for real-time monitoring.
- Often used in industrial or high-frequency monitoring scenarios.
Water Sampling Method for Chemical Analysis
Accurate chemical analysis requires following a systematic water sampling procedure. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
-
- Preparation
- Identify the purpose of sampling and the parameters to be analyzed.
- Select appropriate water sampling equipment, such as bottles, filters, and samplers, made from inert materials to avoid contamination.
- Site Selection
- Choose sampling points that accurately represent the water source, considering factors like flow rate and proximity to pollution sources.
- Choose sampling points that accurately represent the water source, considering factors like flow rate and proximity to pollution sources.
- Collection
- Rinse the sampling container with the water being sampled unless it requires a preservative.
- For surface water, immerse the container below the surface to avoid debris. For groundwater, use pumps to draw samples from wells.
- Preservation
- Add preservatives, if necessary, to stabilize specific chemicals.
- Store samples in a cool, dark environment to prevent degradation.
- Labeling
- Clearly label each sample with the collection date, time, location, and other relevant details.
- Clearly label each sample with the collection date, time, location, and other relevant details.
- Preparation
- Transportation
-
-
- Transport samples to the laboratory as quickly as possible, maintaining the required storage conditions.
- Transport samples to the laboratory as quickly as possible, maintaining the required storage conditions.
-
- Documentation
-
- Maintain a chain-of-custody form to ensure traceability and accountability during sampling water for chemical analysis.
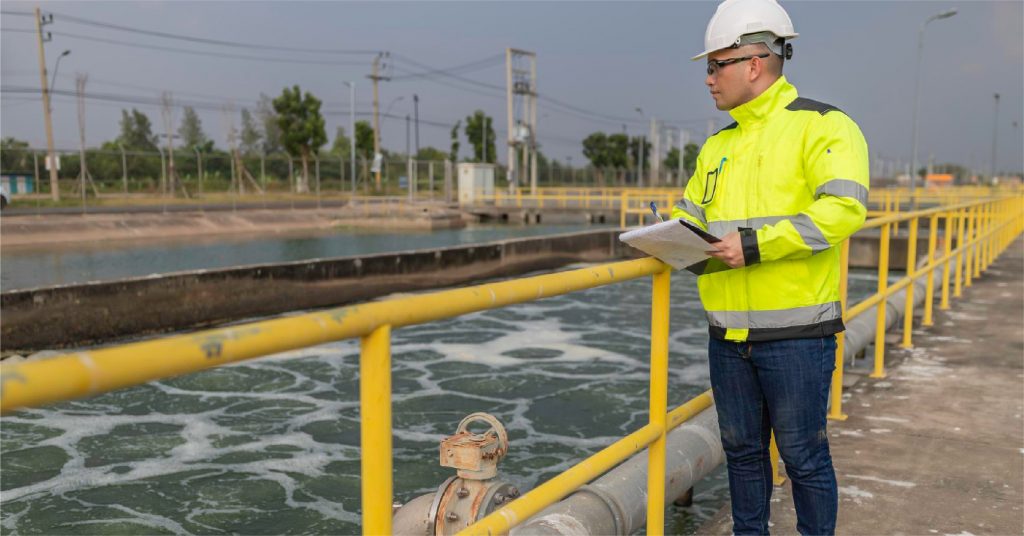
Waste Water Sampling Best Practices
Wastewater sampling presents unique challenges due to the variability in composition and flow rates. Adopting best practices ensures accurate results:
- Use Specialized Equipment
- Select water sampling equipment designed for wastewater, such as automatic samplers or bailers for difficult-to-access locations.
- Time-Weighted Sampling
- Collect samples at regular intervals to account for fluctuations in wastewater composition.
- Volume Proportional Sampling
- Match the sample size to the flow rate of the wastewater for representative results.
- Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow safety guidelines when handling potentially hazardous wastewater.
- Regular Calibration
- Calibrate instruments like pH meters and flow sensors before use to ensure accurate measurements.
Ion Exchange’s Impact on Sustainable Water Management
Ion Exchange is a global leader in water treatment and purification solutions, playing a pivotal role in conserving water resources and ensuring safe water supplies. The company offers various services, including water sampling and analysis, to help industries, municipalities, and communities monitor and improve water quality.
-
Water Treatment Solutions
For over six decades, Ion Exchange has delivered an extensive range of advanced water treatment solutions to industries, institutions, municipalities, and communities worldwide. Their solutions cover every stage of water treatment, including clarification, filtration, disinfection, and post-treatment processes, ensuring water meets stringent quality standards for various applications. Their offerings include:
- Raw water treatment
- Process treatment
- Post-treatment
- Drinking water treatment
-
Process Separation and Purification
Ion Exchange has pioneered the innovative application of membrane and ion exchange processes for separation, purification, and concentration needs across industries, including food and beverages, dairy, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. These technologies have enhanced process fluid separations, improved product quality, and addressed the removal of specific contaminants from groundwater, surface water, and complex wastewater.
- Ion exchange processes
- Membrane processes
- Ion exchange membrane processes
Conclusion
Water sampling is a fundamental component of quality control for any industry that relies on water for production or discharge. Through consistent sampling and adherence to proper water sampling procedures for chemical analysis, industries can maintain water quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect the environment. By using appropriate water sampling equipment and conducting regular wastewater sampling, organizations demonstrate their commitment to safety and sustainability.
Connect with Ion Exchange’s water treatment specialists for expert guidance on selecting the best water sampling equipment.